- Dialectical Behavioral Training Homework
- What Is Dialectical Behavior Therapy
- Dialectical Behavioral Training
- Dialectical Behavior Training
- Dbt Therapy Training
- Dialectical Behavioral Training Home Health
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy In A Nutshell
As Selena Gomez seeks treatment for anxiety and depression, she is reportedly once again turning to dialectical behavior therapy.
Launching Dialectical Behavior Therapy In Jordan. British Isles DBT Training are excited to be collaborating with Behavioral Tech and the Maria Den Braven Centre to deliver an introductory workshop and launch event in DBT in 2020, the first of its kind in Jordan. Dialectical Behavior Therapy, or DBT, combines talk therapy and behavioral therapy to help patients manage negative emotions, and learn interpersonal and communication skills. Unlike CBT which takes a more holistic approach to a patient’s belief system, DBT is focused on four main areas.
The singer is now undergoing DBT, a type of psychological care she has praised before.
“DBT has completely changed my life,” Gomez said in the interview. “I wish more people would talk about therapy.”
What is DBT?
Dialectical behavior therapy is heavily based on cognitive behavioral therapy, or talk therapy.
It promotes both acceptance and change in a patient, which seems contradictory, thus the reference in its name to “dialectical,” defined as the integration of opposites.
DBT was developed in the 1980s by Marsha Linehan, a psychology professor at the University of Washington. She originally designed the approach to treat suicidal behaviors, but it has since expanded to treating borderline personality disorder and other “severe and complex mental disorders,” Linehan’s biography noted. She herself struggled with mental illness and vowed to help herself and others.
How does DBT work?
Patients who undergo DBT receive both one-on-one and group therapy. The goal is for them to “get out of hell” and build “a life worth living,” which can mean different things to different people, Linehan said.
She recognized it wasn’t enough for patients to be listened to and understood in therapy — they also had to receive instruction on how to change. So the program teaches patients various life coping skills, including:
- how to stay present in the moment
- how to tolerate mental pain in difficult situations
- how to ask for what they want
- how to change the emotions they want to change — this may be the most critical part of the entire treatment, Linehan said.
Studies show DBT can be “effective at producing significant and long-lasting improvement for people experiencing a mental illness,” National Alliance on Mental Illness noted.
The approach has also shown promise in treating people with substance abuse. You can find a certified program or therapist through the DBT-Linehan Board of Certification.
Excerpted from “What is dialectical behavior therapy? Selena Gomez’s treatment explained” on the Today show website. Read the full story.
Source: Today | What is dialectical behavior therapy? Selena Gomez’s treatment explained, https://www.today.com/health/what-dbt-dialectical-behavior-therapy-selena-gomez-treatment-t139722 | © 2018 NBC Universalh6>
A screening can help you determine if you or someone you care about should contact a mental health professional. Clinical Services Coordinators can arrange a free 30 minute Care Consultation so you can explore options with an expert. Call or email our Clinical Services Coordinators at 650.688.3625 or careteam@chconline.org to set up an initial Consultation appointment.
The DBT belongs to the third generation therapies or contextual therapies, and has been in recent years one of the important contributions to cognitive behavioral therapy as well as in the field of psychotherapy in general. It was the first psychotherapeutic treatment that demonstrated effectiveness in controlled clinical trials.
The TDC was developed by Marsha M. Linehan and her team in the 90s, with the aim of attending to the suicidal, suicidal and parasuicidal behaviors of people like those with borderline personality disorder, where the constitutional basis of the disorder is the high emotional reactivity and the lack of regulation.
Behavioral Dialectical Therapy
The difference between suicidal and parasuicidal behaviors is that the former are deliberate acts with fatal outcome that a person tries and carries out in full awareness of the definitive consequences of that act. And the second ones are acts with a non-fatal outcome that the individual tries without the intervention of others.
Borderline patients present cognitive-behavioral deficits in several aspects such as interpersonal relationships, control of emotions, and tolerance of suffering.
It is true that, although that was the main objective, adaptations have now been made to apply it to other populations, apply them to patients with other comorbid disorders, as well as eating disorders and chronic depression in elderly people, but these adaptations can only be considered in experimental phase.
Differences between behavioral dialectical therapy and cognitive behavioral therapies
Although behavioral dialectic therapy collects cognitive and behavioral techniques in its procedure, there are notable differences regarding the following aspects:
- The TDC attaches great importance to the acceptance and validation of the behavior of the patient and the therapist in the present moment (influences of the third generation therapies).
- It works with the behaviors that interfere in the therapy.
- The therapeutic relationship acquires a relevant role in the treatment and is considered crucial for the progress of the TDC. This relationship combines acceptance with change, flexibility in terms of limits, emphasis on skills and acceptance of deficits.
- Emphasis on the radical acceptance of behavior and reality. This acceptance implies the absence of a value judgment that is not passive or resigned, but is committed to the change.
The theoretical foundation of behavioral dialectical therapy
Dialectical behavioral therapy, which includes a dialectical-cognitive-behavioral approach, moves away from Beck’s approach and cognitive therapy focused on the modification of cognitive schemes and approaches a more behavioral approach.
This gives more importance to the reinforcing aspects of behavior and takes into account a variety of theoretical and technical sources that justify its consideration as an integrating model, including behavioral science, dialectical philosophy and Zen practice ( mindfulness).

Dialectical philosophy refers to the dialectic / dialogue that occurs between nature, reality and human behavior. The fundamental principle is that established between change and acceptance. This is fundamental to understand the borderline personality disorder, because the thought, behavior and dichotomous emotions characteristic of these people are dialectical failures.
The center of action of the therapist is a function of dialectical processes. This plays with a balance between trying to change the patient, working on the goals of the treatment, supporting the strengths and accepting the weak. This involves validating your experience, understanding what you feel and do, and not reproaching your mistakes.
Linehan’s theoretical approach is based on a biosocial approach, from where he conceptualizes borderline personality disorder. This is conceptualized as an emotionally vulnerable child, presenting a dysfunction of the emotional regulation system, product of the interaction between biological aspects and an environment that invalidates emotional expression.
The subject is very sensitive to emotional stimuli, and has a tendency to experience very intense emotions and difficulties with regard to returning to their emotional baseline. The difficulties in emotional modulation are related to this high reactivity, the deficit in regulating emotions causes them to present an exaggerated emotional reaction.
As time passes, people develop an important fear to experience these emotions and resort to avoidance strategies such as self-injurious behaviors (cut, burn ??), substance use or maladaptive eating behaviors, these serve to mitigate the emotional and physical pain , and momentary relief is a negative reinforcement for the patient, who will resort to such behavior in the future, maintaining the dysfunctional pattern.
To this emotional vulnerability of biological origin, joins the psychosocial or environmental factor. For Linehan, the environment that surrounds us is invalidating and has its effects on the development of personality that occurs in childhood and adolescence.
In the case of subjects with borderline personality disorder, which was focused at the time of performing this therapy, the environment is preceded by a parenting pattern that responds with inappropriate or non-contingent responses to the communication of intimate experiences.
If a person experiences an intense emotion such as sadness, the environment that surrounds him makes him see that he is wrong in describing that emotion he experiences, and that in reality this is based on his unacceptable personality characteristics, which make him Express yourself like that. For example, a child who begins to cry because his favorite toy has been broken and the response of his parents will be enough to make you crybaby ?? Or, a child, who is thirsty and asks for water from his mother, and she responds to him? You can not have thirst again, you have drunk for five minutes?
The problem arises when the person is emotionally vulnerable, that is, when he has difficulty regulating his emotions and he is told to control himself, that it is not okay for him to express his affections like that, and that he does not know how to react to events. In such an environment, it is often necessary for the person to express an emotion with great intensity and in an extreme way, then the environment responds, and reinforces that intense expression, while punishing the expression of negative emotions.
On the other hand, the message sent by the environment of ?? you do not express yourself, if you want one can get to control ??, favors that it is very difficult to tolerate the discomfort, that the individual does not trust their emotions and that invalidates them.
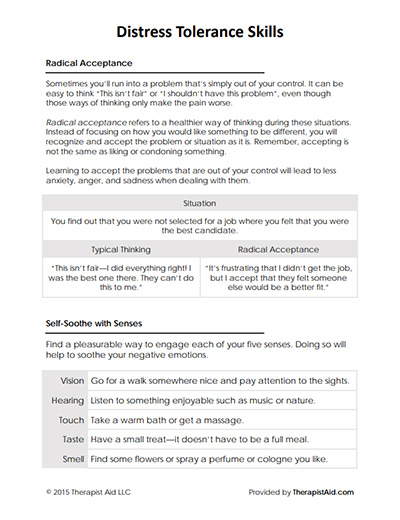
Consequently to the difficulty in regulating the emotions there is an interference in the social relations that the patient establishes, originating chaotic relationships, based on the impulsiveness and the outbursts of extreme negative emotions (eg anger, sadness ??).
Phases of the dialectical-behavioral therapy
Dialectical behavioral therapy develops in three phases, namely pretreatment, treatment and post-treatment.
The pre-treatment phase is the most important, since it is the one where the structure of the program will be exposed, emphasizing the establishment of limits that will guide the therapy.
The patient will be guided about the therapy, the program and the importance it can have in his life. The therapeutic relationship will be established and the cohesion of the group will be built. Goals will be set, explaining the rules of operation of the program to respond to misconceptions that participants may have, and they will be asked to approve and sign the treatment contract.
Some of the rules to comply with are the following:
Dialectical Behavioral Training Homework
- Those who leave therapy will not be able to return to it until it is over. And if they are going to be late for the session or can not go to the session, they should call ahead.
- All participants must follow an individual therapy apart from the group.
- If they go to therapy after having consumed alcohol or drugs, they will not be able to participate in the session.
- All the information obtained during the sessions, as well as the names of these, must be confidential.
- It is forbidden to establish private relationships between clients outside the training sessions, and those who have sex with each other, may not be part of the same training group.
- Patients will not be able to talk about previous suicidal behaviors with others outside the session and if they have any suicidal tendencies and call other people to request help, they should be willing to receive such help.
The treatment phase consists of an individual and a group format a week, as well as telephone consultations between sessions to help patients generalize the skills learned and use them in daily life. Next, I will comment on the formats in the structure section.
Finally, the post-treatment phase includes the self-help groups, composed of patients in advanced stages of the program and who are oriented to help them reduce the likelihood of a crisis and to achieve vital goals, maintain the achievements obtained and relapse prevention.
Structure of the TDC
Individual therapy and group therapy are combined and there are also treatment manuals that allow standardization of interventions.
The TDC adopts strategies pertaining to cognitive-behavioral therapies such as exposure, contingency management, skills training, problem solving, cognitive therapies, and pertaining to third-generation therapies such as mindfulness. In addition, acceptance is emphasized as the main objective for the therapy to be successful. This acceptance must be compromised.
Group therapy is carried out in sessions lasting two and a half hours, once a week, for a minimum of one year. The groups are composed of 6 to 8 patients and two therapists. It focuses on a psychoeducational approach, emphasizing the acquisition of behavioral skills such as interpersonal effectiveness, emotional regulation, tolerance to discomfort, meditation and self-control.
Individual therapy usually lasts one hour, and is done once a week. The motivation of the patient and the post-traumatic stress problems that they usually have are largely worked on. Telephone calls are intended to generalize skills to specific situations in the patient’s life.
What Is Dialectical Behavior Therapy
The objectives of individual therapy are hierarchical and imply an order of priority. It is required that, in order to address a later objective, problem behaviors with a higher priority should not occur. For example, it would not be possible to intervene in the quality of life of a patient if the behavior has not been intervened by the requirement that in order to treat a later objective there should not be incidences of problem behaviors with a higher priority. The objectives are the following:
- Decrease or elimination of suicidal or parasuicidal behaviors.
- Decrease or elimination of behaviors that interfere with therapy.
- Decrease or elimination of behaviors that interfere with the quality of life.
- Acquisition of behavioral skills, replacing the previous ones.
- Reduction of the effects of post-traumatic stress to discover and reduce the effects of physical and emotional sexual childhood traumas.
- Increased respect for oneself.
- Obtaining individual goals that the patient brings to therapy.
Dialectical Behavioral Training
Functions of the treatment program
The treatment program responds to five main functions:
- Enhance the patient’s capacity through the use of different techniques such as skills training, modeling, behavior testing?
- Increase patient motivation by promoting the application of new learning to different situations, using contingency management, exposure?
- Promote generalization to other contexts, transferring new skills to more difficult natural and social contexts, relying on live exhibitions, through telephone consultations?
- Structure the environment, through the application of what has been learned in family and bonding situations.
- Enhance the abilities of the therapist, developing specific skills, supervising the level of being at work, supervision by others.
Techniques used
Dialectical Behavior Training
To achieve the objectives proposed in this individual therapy, different strategies are used that can be grouped into dialectical, nuclear, stylistic, case management, integrating techniques. These will be used in different degrees and will be combined depending on the case. In its application, important elements are developed to achieve the objectives and help the therapist in his relationship with the patient.
Dialectical and nuclear strategies work as an organizing element of therapy and balance attempts at change with acceptance. On the other hand, the validation strategy consists of looking for the elements that make the response of the maladaptive patient understandable and valid, although it needs modification.
The stylistics are those referring to the communicative and interpersonal style necessary and appropriate for therapy. Case management specifies how the therapist should interact and respond to the social network in which the patient is immersed. And the integrators, focus on the way to handle the problematic situations that arise when working with the borderline personality disorder.
In group therapy, other types of strategies are used, such as mindfulness skills, discomfort tolerance skills, emotional regulation skills, and interpersonal skills.
The former serve to enhance the learning of other skills; the second are aimed at the person to tolerate difficult and painful situations, without adding further discomfort; the third ones are oriented to the modulation of the emotions and the last ones are oriented to teach to apply specific abilities of resolution of interpersonal, social and assertiveness problems to modify aversive atmospheres and obtain their objectives in the interpersonal encounters.
Dbt Therapy Training
Conclusions
Dialectical Behavioral Training Home Health
Within the third generation therapies, the dialectic behavioral therapy has obtained the best results, fulfilling criteria to become a treatment with empirical support.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy In A Nutshell
Also Read: The Psychological Interview The Best Evaluation Method?
It is of great value to consider that a therapy with a point of view very different from traditional therapies, with characteristics that are more artistic, and perhaps less rigorous, is bearing so much fruit in the field of personality disorders.

